Today, around 3.6 million Malaysians suffer from diabetes, and by 2025 it is expected that nearly 1 in 3 Malaysian may suffer from diabetes.
Even though so many people in Malaysia suffer from diabetes, not many are informed about the disease and its dangers, or worse, they don’t think it’s a very serious problem. However, these statistics should not be taken lightly, so let’s start by decoding what exactly is diabetes.
To understand diabetes, we first need to understand the role sugars play in our bodies.
During a meal, carbohydrates consumed, such as rice, are broken down into glucose, a type of sugar. This glucose is then processed by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin helps transport the glucose from the blood into the cells where they are used as fuel to power the body.
Diabetes occurs when the body is unable to produce insulin (this is known as Type 1 diabetes) or has trouble producing enough insulin (this occurs in Type 2 diabetes) to break down the glucose. This leads to a build-up of sugar in the blood stream, which in turn increases the risk of other illnesses such as heart disease, stroke, and more.
Early signs of diabetes to keep a lookout for include frequent urination, sudden weight loss, constant thirst, and even numbness in feet and hands. The last symptom is especially important as cuts and bruises on the feet can go unnoticed and fester into painful diabetic foot ulcers that take months to heal.

Unfortunately, there is no singular cause for diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, genetic factors are thought to play a role, while in Type 2 diabetes studies have found that people with a combination of genetic factors and being overweight leads to a higher risk of getting diabetes.
No, as there is no cure for diabetes. However, there are treatment options:
Type 1 diabetes: Insulin injections are used as a replacement since the body is unable to produce it. However, there can be some side effects to insulin therapy such as weight gain, low blood sugar, and rashes or scars at the site of injection.
Type 2 diabetes: A combination of diet, exercise and in some cases, medication is used to help people manage their condition.
Ensuring that you have good lifestyle habits such as eating a healthy diet with less processed sugar and getting plenty of exercise in your daily routine is key to reducing the risk of getting diabetes.
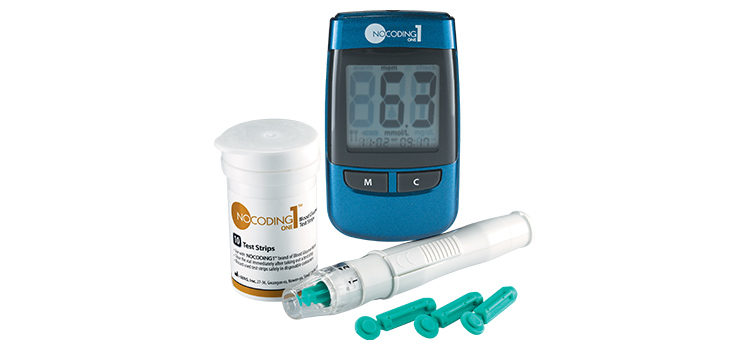
Additionally, if diabetes is common in your family, it’s important to keep a close eye on your blood sugar levels. Invest in a user-friendly blood glucose monitor, also known as glucometer, such as iSens NoCoding1 Blood Glucose Monitor which takes only 5 seconds to read your glucose levels – now you can monitor your blood sugar levels in the comfort of your own home.

Don’t forget to pick up iSens NoCoding1 Test Strips (25 strips per bottle) that are designed to be used together with the Glucose Monitor. Each easy-to use strip includes a confirmation window to make sure the blood sample is enough for more accurate readings.